How does Coronavirus Outbreak Impact on the Global Economy?
Since the first case of COVID-19 was identified in the central China city, Wuhan last December, the virus outbreak has spreaded across the world, infected more than 110,000 people and recorded more than 4,000 death in at least 110 countries and territories globally, according to the World Health Organization. This ongoing spread of COVID-19 has become biggest treats to the global economy and financial markets.
China, where the majority of the confirmed cases are, has reported more than 80,000 infections in the mainland so far. To contain the COVID-19 outbreak, Chinese authorities locked down cities, restricted movements of millions and suspended business operations. The decision will slow down the world’s second-largest economy and drag down the global economy along the way.
The situation worsen when the disease is spreading rapidly around the world, with countries like Italy, Iran and South Korea reporting more than 7,000 cases each. Other European countries like France, Germany and Spain have also seen a recent spike beyond 1,000 cases.
Downgrades in economic forecasts
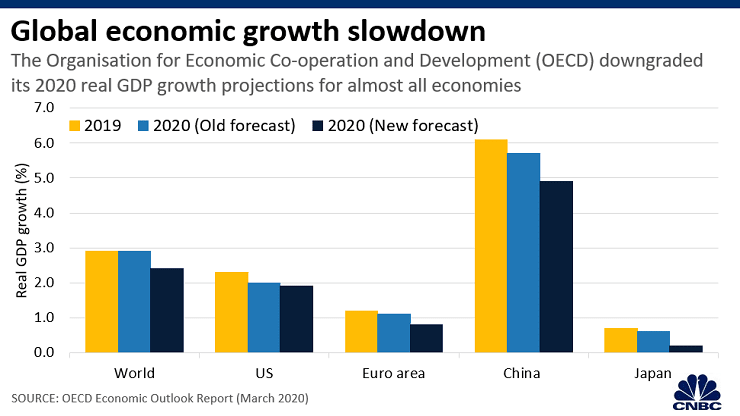
The outbreak has led major institutions and banks to cut their forecasts for the global economy. One of the latest to do so is the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Based on the chart, China’s gross domestic product growth saw the largest downgrade in terms of magnitude, according to the report. The Asian economic giant is expected to grow by 4.9% this year, slower than the earlier forecast of 5.7%, said OECD. Meanwhile, the global economy is expected to grow by 2.4% in 2020 — down from the 2.9% projected earlier, said the report.
Slowdown in manufacturing activity
The manufacturing sector in China has been hit hard by the virus outbreak. The slowdown in Chinese manufacturing has hurt countries with close economic links to China, such as Vietnam, Singapore and South Korea. Several analysts predict that the factories in China will take longer than expected to resume operations. Along with a rapid spread of COVID-19 outside China, means that global manufacturing activity could remain subdued for longer, economists said

Services contraction
The virus outbreak affects the country’s services industry as reduced consumer spending hurt retail stores, restaurants and aviation among others. China is not the only country where the services sector has weakened. The services sector in the U.S., the world’s largest consumer market, also contracted in February, according to IHS Markit, which compiles the monthly PMI data

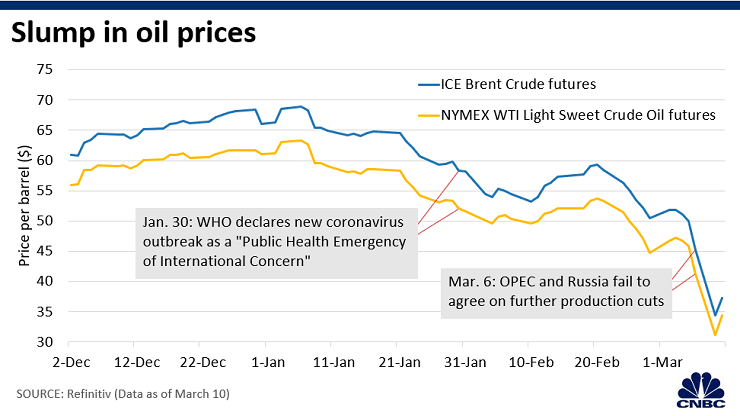
Declining oil prices
China, the epicenter of the coronavirus outbreak, is the world’s largest crude oil importer. A reduction in global economic activity has lowered the demand for oil, taking oil prices to multi-year lows.
Sourced from here.
Related posts
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.





